What Is Google Penguin? Redefining Quality Content & Links
Hand off the toughest tasks in SEO, PPC, and content without compromising quality
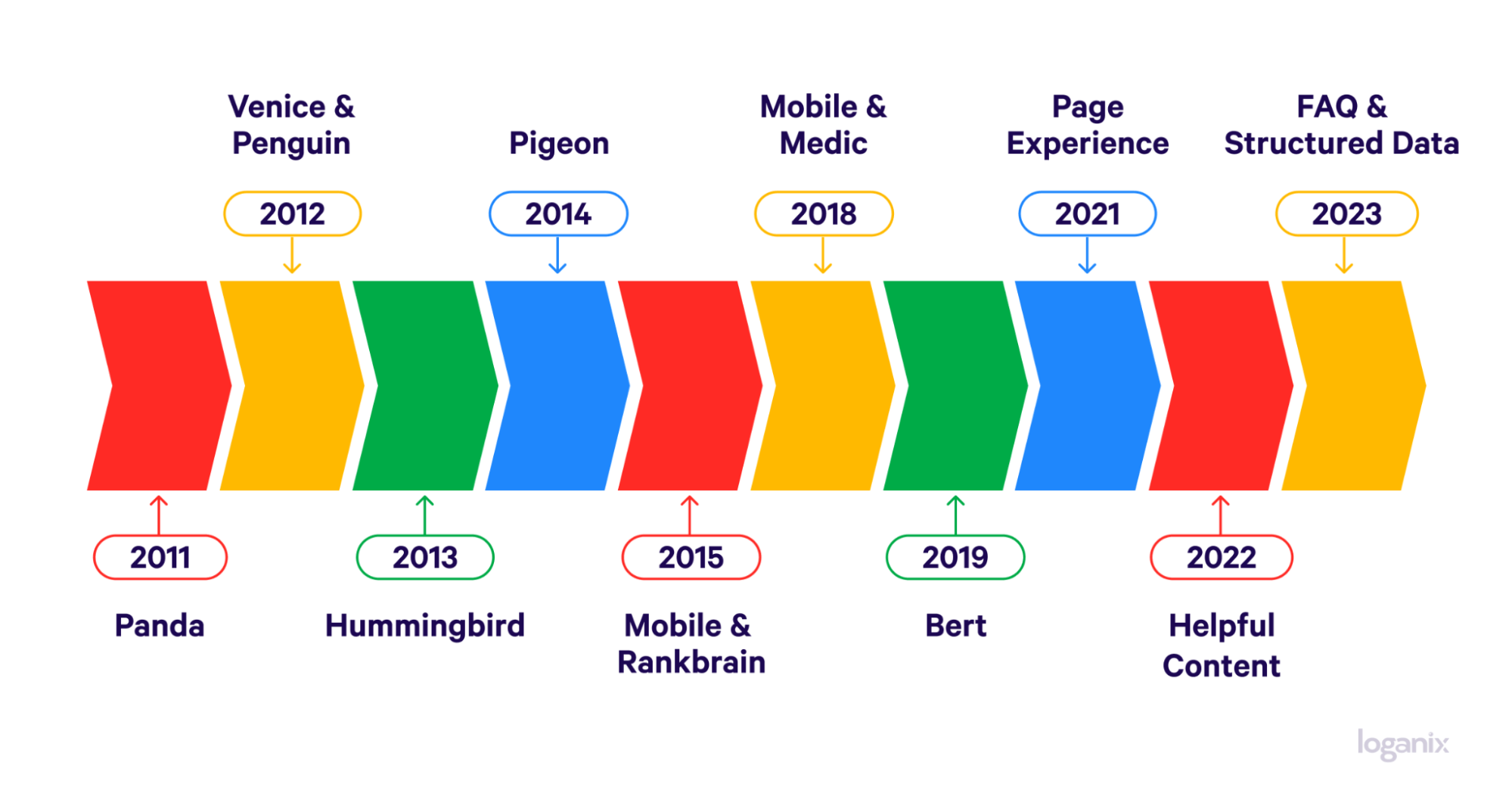
Explore ServicesLaunched back in April of 2012, the Penguin update was a line drawn in the sand. A clear signal that Google was committed to promoting quality content and natural link-building practices while penalizing websites that resorted to manipulative tactics such as keyword stuffing and unethical link schemes.
Google clearly views Penguin as a successful endeavor—it’s now been made part of the search engine’s core algorithm and operates in real-time, meaning changes to a website are assessed by Penguin almost instantly, making its impact continuous and immediate.
To ensure you don’t find yourself on the receiving end of any Penguin wrath, in this guide, we’ll
- answer the question, “What is Google Penguin,”
- explore its intricacies and its implications for your website,
- and provide insights on how to recover if your site has been hit by a Penguin penalty.
What Is Google Penguin?
Google Penguin was an algorithmic update to Google’s search engine. Its primary function is to combat web spam and manipulative link-building practices employed by black hat practitioners, ensuring that the search engine results pages (SERPs) are filled with high-quality, relevant content.
So how exactly does Penguin function? The update works by analyzing the links on a website to determine whether they appear natural or manipulated. It achieves this by looking at factors such as the quality of the sites being linked to, the relevance of the linked content to the source page, and a link’s anchor text.
Learn more: Interested in broadening your SEO knowledge even further? Check out our SEO glossary, where we’ve explained over 250+ terms.
Why Is Google Penguin Important?

The importance of Google Penguin cannot be overstated—its introduction was far-reaching. When the update was first rolled out, it had a significant impact on search queries, affecting an estimated 3.1 percent of queries in English and an even higher percentage in languages that were deemed “highly spammed.”
A massive announcement was made in September 2016. The fourth iteration of Penguin—Penguin 4.0—was made part of Google’s core algorithm, meaning changes to a website’s link profile are evaluated in real time, and the impact on search rankings is immediate. Prior to this, webmasters had to wait for the next Penguin update to see the effects of their SEO efforts or recover from a penalty.
As frightening as the possibility of real-time penalties was, it wasn’t all bad news. The new real-time nature of Penguin extends to the recovery process as well. If a penalized website makes the necessary changes to remove or disavow the offending links, it can recover its search rankings as soon as those changes are detected by Penguin, giving webmasters the ability to respond quickly to penalties and make necessary adjustments to their SEO strategies.
Penguin 4.0 also brought about a more granular approach to penalties. Instead of penalizing an entire website, it can now target specific pages or sections of a site that are found to be in violation of Google’s guidelines, meaning a single page with poor SEO practices would no longer drag down the entire website’s ranking.
Another significant change with Penguin 4.0 was how it deals with bad links. Instead of demoting websites for having bad links, it simply discounts them. So, while the entire website won’t be penalized as with previous iterations of Penguin, this adjustment means that any offending links will simply be disregarded. Consequently, these links will no longer provide any SEO advantage.
This approach serves three purposes: 1) it discourages black hat link-building practices by rendering them useless, 2) provides a more forgiving environment for websites that may have inadvertently obtained poor-quality links, and 3) eliminates “negative SEO attacks,” where a competitor harms a website’s rankings by linking to them from spammy or low-quality sites.
Identifying a Google Penguin Penalty
Unfortunately, Google doesn’t go out of its way to inform you if your website has been penalized. Thankfully, though, there are methods you can use to determine if your site has been impacted by a Penguin penalty. The approach involves a blend of careful observation, intuition, and the use of Google Search Console.
The first thing to keep in mind is that, as we touched on, Google Penguin operates on a page-specific basis, meaning it impacts individual pages rather than your entire website. Consequently, if Penguin has penalized your site, you’ll likely observe a substantial decrease in traffic to specific pages.
With this in mind, here’s how to identify a Penguin penalty:
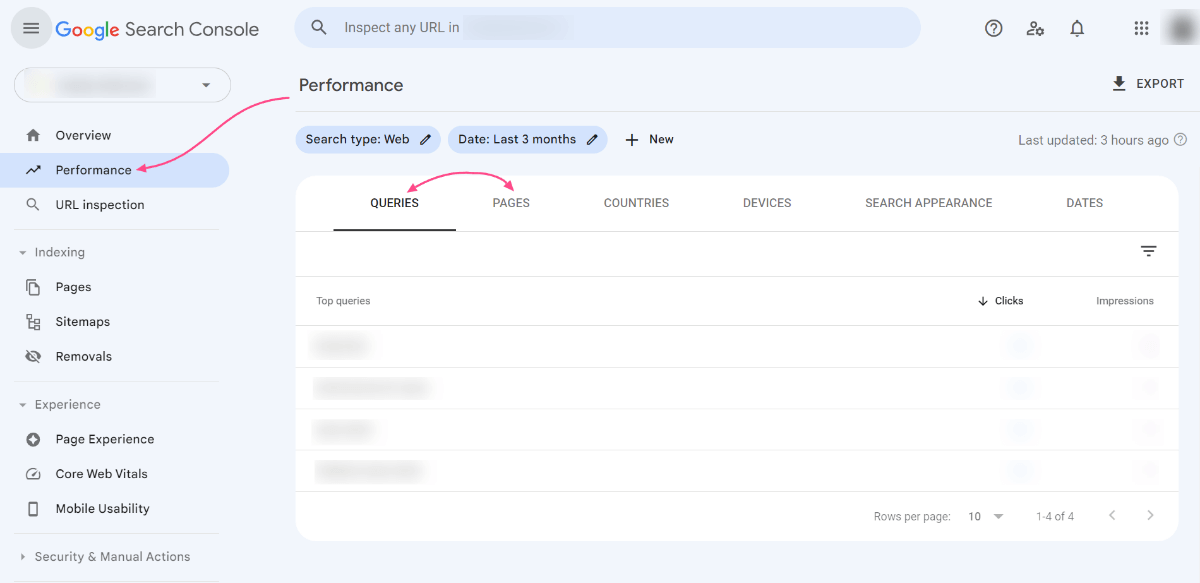
- Check Google Search Console: Log into your Google Search Console account and navigate to the “Performance” section, then click on the “Pages” tab. Here, you can view individual web pages’ performance data, including clicks, impressions, and average position for specific search queries. A sudden drop in these metrics could indicate a Penguin penalty.
- Analyze Keyword Rankings: Pay close attention to any sharp declines in your website traffic. If you notice a significant drop, particularly for a specific keyword, this could be a sign that your site has been penalized. Once again, from the “Performance” section, you can do this by clicking on the “Queries” tab.
Recovering from a Google Penguin Penalty
Here’s how to recover from a Google Penguin penalty:
- Identify Low-Quality Links: The first step in recovering from a Google Penguin penalty is to master the art of identifying low-quality links that are potentially harming your site’s rankings. Hot tip: look for links from low-quality, spammy sites or backlinks that originate from content that’s not relevant to your own.
- Remove Bad Links: Once you’ve honed your identification skills, the next step is to remove the bad or “toxic” backlinks. You can contact the owner of the site and request they remove it, but this is often a long shot. If we’re being honest, it’s probably best just to skip this process and try your hand at the next step.
- Disavow Bad Links: If you’re unable to get a link removed, you can use Google’s Disavow tool to tell Google that you don’t want certain links to be considered when assessing your site.
- Improve Your Site’s Content: Google Penguin penalizes sites with poor-quality content. So, improving the quality of your content can help you recover from a penalty. Make sure your content is original, relevant, and provides value to your users.
- Wait for Google to Recrawl Your Site: After you’ve made these changes, you’ll need to wait for Google to recrawl your site and update its index. This can take several weeks up to a few months or more.
To learn how to identify bad links and disavow them, check out our toxic links guide.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Navigating the complexities of Google’s algorithms and updates is both challenging and time-consuming. That’s where Loganix comes in. Our team of SEO experts has a deep understanding of Google’s updates, including Penguin. We offer a range of SEO services that can help you recover from penalties, build high-quality backlinks, and improve your search rankings.
🚀 Don’t let Google Penguin keep you in the cold—check out our suite of SEO services today and get your website’s rankings back on track. 🚀
Hand off the toughest tasks in SEO, PPC, and content without compromising quality
Explore ServicesWritten by Adam Steele on January 5, 2024
COO and Product Director at Loganix. Recovering SEO, now focused on the understanding how Loganix can make the work-lives of SEO and agency folks more enjoyable, and profitable. Writing from beautiful Vancouver, British Columbia.





