What Is CSS?

Hand off the toughest tasks in SEO, PPC, and content without compromising quality
Explore ServicesPerhaps you are not a programmer or in the web development field, but you have most likely heard of HTML. It’s the most basic markup language, and it’s been around since the 1990s.
CSS is an excellent programming language for beginners to learn since it is simple to understand and there are several resources and tutorials available that demonstrate how to use it.
CSS, on the other hand, may be unfamiliar to you. It’s an equally essential aspect of programming language, and CSS, together with HTML and JavaScript, is one of the three fundamental pillars of web technology.
But what exactly is CSS, how does it operate, and why is it so important? Continue reading to find out more!
What Is CSS?
CSS is an abbreviation for Cascading Style Sheets. It is a style sheet language that controls many of a web page’s visual elements.
Prior to CSS, developers (Web designers) had to format their information on a page using HTML code, and even then, the content was limited. HTML was designed to be only a markup language for linking diverse internet content together. HTML was never intended to be used for page layout.
When HTML 3.2 introduced style formatting elements for characteristics like typefaces, it generated problems for web developers. Programmers would have to go through a lengthy and costly process of writing vast pages of HTML code. If something went wrong on the web page, it was difficult to identify problems in the HTML syntax.
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) recognized this and adopted CSS to resolve the problem. They later formed the CSS Working Group, which was tasked with producing the current version of CSS.
CSS saved HTML and the tech industry by removing all style formatting HTML tags from the page and replacing them with lists of rules known as style sheets.
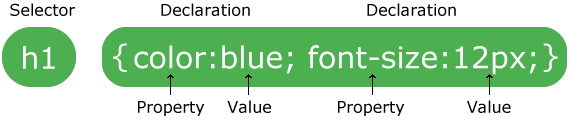
When considering the construction of a home or any other sort of building, HTML symbolizes the fundamental framework of the building: the walls, stairs, and doors. CSS would reflect the building’s paint, decorations, and style. While HTML offers the basic structure of your webpage, CSS provides the style that distinguishes it from other websites on the Internet.
CSS syntax is straightforward, consisting of a plain text document known as a style sheet. Rules are style sheets that are divided into blocks of code. All CSS files are written in style sheets, as the name implies. A style sheet instructs the web browser on how to display the content being viewed.
CSS3 is the CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) version that replaced CSS2. It added additional selectors and attributes that give you more control over page layout and display. Some changes, like the box-shadow property (which allows an element to drop shadow), make it possible to apply visual effects without the requirement for specific pictures.
Furthermore, CSS is distinct from HTML and may be used by any markup language, including SVG, XUL, XHTML (a variation of HTML) and XML (Extensible Markup Language).
So you could be wondering how does CSS work with HTML?
CSS adds style to web pages by interacting with specific HTML components known as HTML elements. The language makes it possible to separate appearance from content. This increases accessibility and speed while processing web pages. It also increases versatility across several sites and eliminates redundancy and effort in HTML coding. CSS is styled in a Microsoft word processor or text editor by developers, and it is linked to HTML in three ways.
External CSS style sheets, the most preferred option, are stored as a distinct separate file with the .css extension from the HTML document. The style rules will then be pulled from a single CSS reference by every HTML page. This technique is advised if you have a number of rules that may be applied to several pages on your website. To use an external style sheet, insert a link tag in your HTML page’s header section that points to your .css file.
Internal style sheets are included in the header part of your HTML file but within a style tag. Internal style sheets are suggested if you have a single page with a few guidelines that differ from the other pages on your website.
Inline style sheets are found within the HTML file’s elements. These are tiny CSS elements that have been put into the code. Inline style sheets should be utilized only when the style is a single code instance throughout the entire website.
To illustrate the importance of how you use CSS, here’s an example of the same page with CSS and without CSS.
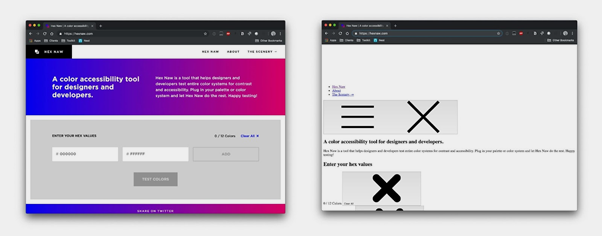
Isn’t it a startling difference? When it comes to general appearance, you’ll notice quite a few variations between the two. CSS causes changes in typeface, font size, font style, and font color. The format of the buttons has been changed, text-align and a blue to pink gradient background color have been placed behind them.
Because of cascading style sheets, each of these aspects is possible. Which appears more appealing to you as a user? It’s simple to understand why CSS is so important.
Why is CSS Important?
CSS has a lot of benefits, including:
1) Increased Page Load Speed
More code equals a slower website load time. CSS also allows you to utilize less code. CSS enables you to use a single CSS rule to apply to all instances of a certain tag within an HTML page. As a result, if your website takes even two seconds longer to load, your bounce rate increases by 50%.
2) Improved User Experience
CSS not only makes websites more visually appealing but also allows for user-friendly formatting. The user experience improves when buttons and content are in logical positions and neatly structured. A well-placed button (CTA) allows users to convert easily, and are able to understand the next step, till the overall goal is met. As a result, a one-second delay in load times might result in a 20-30% drop in conversions.
3) Reduced Development Time
CSS allows you to apply precise formatting rules and styles to numerous pages with a single line of code. A single cascading style sheet can be used on several website pages. If you have product pages that all need to have the same formatting, look, and feel, setting CSS rules for one page will serve for all pages of that type.
4) Simple Formatting Adjustments
If you need to modify the format of a specific set of pages, CSS makes it simple. There is no need to fix each and every page. Simply modify the relevant CSS stylesheet, and the changes will be reflected on all pages that use that style sheet.
5) Device-to-device compatibility
The importance of responsive site design cannot be overstated. Web pages must be completely viewable and readily navigated on all devices in today’s world. CSS and HTML work together to provide the responsive design on mobile, tablet, desktop, and even smart TV devices.
Responsive viewports, media queries, grid views, pictures, and videos may all be implemented with CSS. Your website will appear great on all devices, increasing engagement and conversion rates.
CSS FAQ
Does CSS affect SEO?
CSS is well-known for creating standards-compliant, easily changeable, and fast-loading web pages. CSS, in addition to its well-known features, provides some significant SEO benefits. The following is a list of the key benefits provided by CSS:
- Using CSS, one may create menus with internal links by utilizing standard HTML tags such as <ul> and <a>. This allows search engines to quickly identify the connections and aids in the efficient and deeper crawling of the site.
- CSS lowers the code-to-content ratio by making web pages lighter. This can make your site simpler to read not only for users but also for bots, resulting in improved indexing.
- Using CSS, you may separate content and presentation. This lets you test alternative copy and presentation strategies to see what converts the best.
- CSS reduces the time spent on website maintenance and frees up webmaster resources. It enables you to incorporate newer content and create new SEO tactics.
Is inline CSS good for SEO?
An inline CSS style is used to create a distinctive style for a single HTML element. Inline CSS helps make use of an HTML element’s style attribute.
Inline CSS is not good for SEO, since it does impact the loading speed of any website, and it also affects SEO because SEO is dependent on ranking. As a result, if your site has loading and performance issues, it will have an impact on its SEO ranking.
In addition, Inline CSS may block some assets. if it blocks any valid content that needs to be exposed, that may impact SEO value.
Google’s take on it is:
Allow Google to crawl all site assets that would significantly affect page rendering, such as CSS and JavaScript files that affect the comprehension of the pages, to help Google completely comprehend your site’s content. The Google indexing system displays a web page as it would appear to a user, including pictures, CSS, and JavaScript files.
Summary
Hopefully, this article has given you a better understanding of CSS.
In the SEO web design process, CSS provides the presentation, character, and personality of a website. You wouldn’t want to go outdoors looking drab and uninteresting. You wouldn’t want your home, car, or anything else that reflects who you are to have a styling that is tasteless. Even if you only place a flag on your car or a wreath on your front door, it adds a touch of flair.
The same is true for your websites. CSS allows you to experiment with colors, spacing, fonts, and layouts to create visually appealing web pages for the general audience. It also reduces developer workload by isolating style formatting from the actual structure of the webpage.
So that if you run into any difficulties with your code, you can easily discover out where the problems are by using distinct coding files. There’s no need to spend hours figuring out where the syntax went wrong in a large document.
Since this article sounds too technical, Loganix is here to help you implement CSS for your website, thus it will help you create an easy user interface with a great user experience for your visitors.
Hand off the toughest tasks in SEO, PPC, and content without compromising quality
Explore ServicesWritten by Adam Steele on October 8, 2021
COO and Product Director at Loganix. Recovering SEO, now focused on the understanding how Loganix can make the work-lives of SEO and agency folks more enjoyable, and profitable. Writing from beautiful Vancouver, British Columbia.





