What Is Indexing in SEO?

Hand off the toughest tasks in SEO, PPC, and content without compromising quality
Explore ServicesThere is little question that SEO is taking longer than ever to produce results (assuming you follow Google’s rules, as we do at Loganix).
As more websites compete for attention, search engines have struggled to keep up with this expansion while remaining focused on presenting the most relevant content to a visitor. As a result, it is critical to understand how search engines work in order to ensure that your site is as search engine friendly as possible.
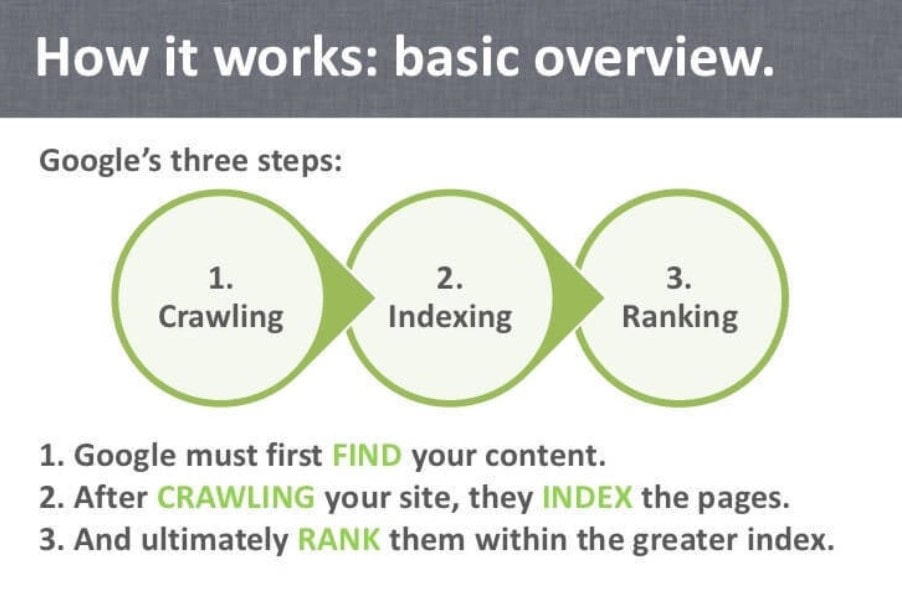
Crawling, indexing and ranking are the three essential steps in delivering search results.
This article will look at what indexing is in SEO, its importance, what Google indexing is, what indexing a web page is, and the difference between crawling and indexing in SEO.
Let’s get right into it!
What Is Indexing in SEO?
The term “indexing” refers to a process of gathering information with the purpose of building an index of pages or other data. This data is sorted depending on certain criteria, such as assigning keywords to a document based on its content.
The index is formed by the produced pages and their corresponding keywords, which allows for easier searching and filtering of information.
Indexing is the technique through which search engines organize content prior to a search in order to provide lightning-fast replies to queries.
Search engines would struggle to find useful content if they had to sift through individual sites for keywords and subjects. Search engines (including Google) instead employ an inverted index, often known as a reverse index.
Modern database management systems (DBMS) use an index to guarantee that when specific keywords are typed, a list of relevant content is presented. Google and other search engines such as Yahoo, and Bing operate in the same manner. When a user enters a search query, the index is searched rather than the entire internet to discover relevant search results.
Indexed pages may appear in Google Search results if they adhere to Google’s webmaster standards.
Why Is Indexing in SEO Important?
If you want to attract more Internet users to visit your website for whatever reason, having your website indexed on Google is critical. For example, if you operate an online business and have a website that acts as your online presence, search engine optimization may provide you with various benefits.
At the same time, the importance of ranking first in organic search has never been higher; 57 percent of B2B marketers and webmasters claim SEO produces more leads than any other marketing endeavor, which is why the SEO/Search business has expanded at such a rapid pace in recent years.
Attract more online visitors, catch their attention, provide them with your offer, create high-quality content, and do anything else that can lead to higher website traffic. The most essential thing you can do to increase the number of visitors to your website is to notify search engines that it exists.
If you want to attract the attention of all internet users in order to generate traffic, you must first understand that the Internet is totally dependent on protocols and the information presented as a result of those protocols.
Because the Internet is a massive information repository, many people mistakenly believe that once their content is submitted, it is instantly exposed to everyone online. Things don’t operate this way, and not everything displays at the same rate. The previously held online content is always the first to arrive.
That is why, while maintaining your website online, it is critical to consider search engines. If you want to ensure that your website receives the attention it deserves, you must first grasp how search engines and their algorithms function. This relates to how people assess and discover your content.
Crawling and indexing are the two main phases in the process of finding and evaluating. It’s really that simple. That is why web indexing has just become so essential. Googlebot is the item that allows every Google search to be primarily responsible for all contemporary searches. It is a large group of crawlers and bots that are linked into a single software that Google uses to provide you with search results when needed.
Indexing FAQ
What is Google indexing?
Indexing, in layman’s terms, is the process of adding web pages to Google search.
So what exactly is the Google index?
Google has a fantastic analogy:
“The Google index is comparable to a library’s index, which includes information on all the books in the library’s collection. The Google index, on the other hand, instead of books, lists all of the websites that Google is aware of. When Google visits your website, it identifies new and modified pages and updates its index.”
Google crawls and indexes your sites based on the meta tag you specified (index or NO-index). A no-index tag indicates that the page will not be included in the online search index.
Every WordPress post and page is indexed by default enabled by the Yoast plugin. Allowing just essential sections of your blog/website to be indexed is a smart way to rank better in search engines. Do not index nonessential archives such as tags, categories, and any other worthless pages.
Organic traffic is the lifeblood of every online business, but you won’t obtain any unless Google indexes your content. To understand what indexing is and why Google does not correctly index some websites, we must first understand Google’s index and how it operates.
Meta robots instructions can be applied in the HTML source and the HTTP header.
Nofollow links are also not crawled by Google. Nofollow links are links with the rel=“nofollow” tag. They impede the transmission of PageRank to the target URL.
What is indexing a web page?
In a word, website indexing is the process through which search engines understand the functionality of your website and each important page on that website. It assists Google in finding your website, indexing it, associating each page with searched subjects, returning this site on search engine results pages (SERPs), and eventually driving the proper visitors to your content.
Consider how an index works in books: it’s a collection of valuable terms and information that adds context to a subject. In the context of search engine results pages, this is exactly what website indexing accomplishes (SERPs).
The internet is not what you see when you use a search engine. It’s the search engine’s index. This is significant because not every page you post online is guaranteed to attract the attention of a search engine. You must perform a few things as the owner of a website in order for it to be included in Google’s index.
Google indexes websites that include a few essential elements. Take a peek at these:
- In accordance with common searches.
- The homepage of the website is easily navigable.
- Other sites on and off your site’s domain link to it.
Because of the usage of particular metatags, you are not “banned” from indexation. This is due to the fact that keywords are similar to pings to search engines: It tells Google in a few words what your page content is about, which may then be communicated back to search queries.
Having keywords is only one of the many criteria Google considers before indexing websites. Other requirements include the absence of “broken” pages as well as a complex web design that inhibits a visitor from simply locating the page or comprehending the issue the page is answering.
If the URL Inspection tool indicates that the URL has not yet been indexed, you can use the same tool to request indexing.
What does indexing mean in search?
A search index assists users in rapidly locating information on a website. Its purpose is to map search queries to documents or URLs that may appear in the results.
Does that seem complicated? Here’s an easier way to put it:
You may have come across an index in a more conventional medium: books. Many large (scientific) books contain an index to assist you to quickly find important content.
An index, which comprises a list of keywords sorted alphabetically, is generally included at the conclusion of the book. Each keyword links to a page where you may discover valuable information about the term.
As an example, suppose you have a book about animals that is several hundred pages long. You want to learn more about “cats.” Look for the keyword “cat” in the index and read up on the sites that are mentioned (p. 17, 89, 203-205).
A search index is similar to one found in a book. It enables the user to rapidly discover relevant information by typing in a term. Of course, a web search index has numerous technological benefits over a book search index and provides excellent tools to assist website users in finding what they are looking for quicker.
What is the difference between crawling and indexing in SEO?
Crawling is the process of following links on a page to new pages and then continuing to locate and follow links on new pages to new pages.
A web crawler is a piece of software that follows all of the links on a page, leading to new pages, and repeats the process until it runs out of new links (backlinks, internal links) or pages to crawl.
Web crawlers are sometimes known as robots, spiders, search engine bots, or just “bots” for short. They are called robots because they have a task to complete, move from link to link, and collect information from each website. Unfortunately, if you imagined a genuine robot with metal plates and arms, these robots do not resemble that. Googlebot refers to Google’s web crawler.
The crawling process must begin somewhere. Google starts with a “seed list” of reputable websites that link to a lot of other sites. They also employ lists of sites visited in previous crawls and sitemaps supplied by website owners.
A search engine’s crawling of the Internet is an ongoing operation. It never truly comes to an end. It is critical for search engines to identify newly published pages or modifications to existing ones. They don’t want to waste time and money on pages that aren’t excellent search result possibilities.
Google gives crawling priority to pages that are:
- Well-known (linked to often)
- Excellent quality
- Regularly updated
- Websites that publish new, high-quality content.
The crawl budget is the number of pages or requests that Google will crawl for a website during a given time period. The number of pages budgeted is determined by the site’s size, popularity, quality, updates, and speed.
If your website wastes crawling resources, your crawl budget will be depleted and pages will be crawled less frequently, resulting in worse rankings. By sending up too many low-value-add URLs to a crawler, a website might accidentally squander web crawler resources. Faceted navigation, hacked pages, on-site duplicate content, endless spaces, soft error pages, and proxies, low quality, and spam content are all examples of this.
Google selects websites for more frequent crawling but does not enable websites to pay for improved crawling. With instructions in a robots.txt file, a website can opt out of crawling or restrict the crawling of specific portions of the site. These rules notify search engine web crawlers which portions of the website they can and cannot explore. Use robots.txt with extreme caution. It is easy to inadvertently restrict Google from all pages on a website. The prohibit commands match any URL route that begins with the path specified.
Indexing, on the other hand, is the process of storing and arranging information found on pages. The bot displays the code on the page in the same manner that a browser would. It catalogs all of the page’s content, links, and information.
Summary
Hopefully, this article has given you a better understanding of indexing in SEO.
Google does not include everything in its index. The figures are astounding. Only 16% of important, indexable pages are indexed. Simultaneously, many huge websites have been fully indexed; an optimized website is easier for Google to index. Indexing is a lot more difficult than making sure a page doesn’t contain a “noindex” tag, a canonical tag, or isn’t blocked by a robots.txt file.
eCommerce websites are especially vulnerable to indexing problems. Websites powered by JavaScript aren’t the only ones that might have indexing difficulties. Unique and new content aids indexing, but duplicate content makes indexing more difficult. Crawling and finding new pages are inextricably linked to ranking signals and indexing.
Google Search Console or Bing Webmaster Tools are essential tools for troubleshooting indexing difficulties, so make use of them.
Hand off the toughest tasks in SEO, PPC, and content without compromising quality
Explore ServicesWritten by Jake Sheridan on December 3, 2021
Founder of Sheets for Marketers, I nerd out on automating parts of my work using Google Sheets. At Loganix I build products, and content marketing. There’s nothing like a well deserved drink after a busy day spreadsheeting.





