What Is Schema?

Hand off the toughest tasks in SEO, PPC, and content without compromising quality
Explore ServicesThere are several SEO actions that can be taken to optimize and improve your web page.
What is the one thing you believe websites might be doing to get an advantage over their competitors?
According to a thorough research study, its implementation will offer you an advantage of four average positions on SERP.
It is possible to do this by adding a tiny bit of code to your webpage known as Schema Markup, which may be obtained at Schema.org. (Schema.org is a collaborative effort by all search engines to add structure to material in order to enhance readability and the display of search results.)
This article will look at what schema is, its importance, why use structured data for SEO, what a schema tag is in SEO, why schema is important in SEO, what schema is used for, and the types of schema markups.
Let’s get right into it.
What Is Schema?
Schema markup is code (also known as semantic vocabulary or microdata) that you may add to your website’s HTML. This microdata assists search engines in better understanding your material, allowing them to provide more thorough and useful results to searchers.
When you add schema markup to your website, it generates a more thorough description for your page, known as a “rich snippet,” which shows on the search engine results page (SERP). In a subsequent part, we’ll go into rich snippets in further depth.
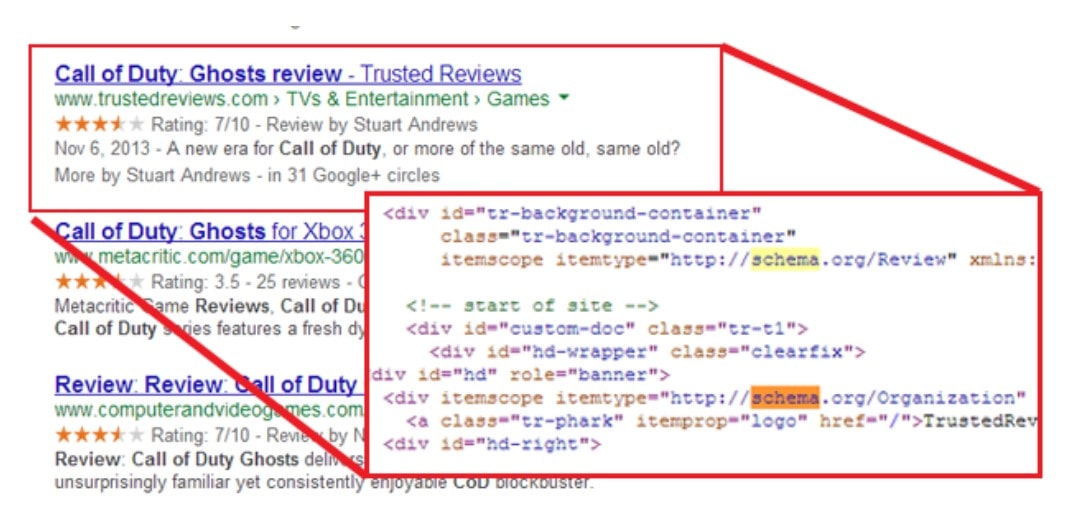
Various search engines, including Google, Bing, Yandex, and Yahoo, have collaborated to create Schema.org.
Why Is Schema Important?
Rich snippets, which frequently have greater clickthrough rates than ‘regular’ search results, are powered by Schema markup. This implies more visitors to your website.
The major goal of the markup, however, is to assist search engines in better understanding your content.
It’s no accident that schema.org, the community behind the markup, was founded a year before Google’s Knowledge Graph—a knowledge store of things and their relationships—was born.
And, you got it, schema markup is one of the major sources of this data. All of the edges that link the nodes above contain actual schema markup characteristics.
This is where we get to the crux of the problem.
Everyone benefits from providing easy-to-read information and connecting the dots about you, your organization, goods, and content. It is significantly more understood by Google than plain text. Users benefit from more relevant search results.
In fact, visual search is desired by 62 percent of Gen Z and Millennial customers more than any other new technology.
Website owners receive rich snippets and have the opportunity to become entities in the Knowledge Graph. Being a part of the Knowledge Graph gives tremendous branding chances in the SERP.
First, when consumers search for your brand, you can receive a Knowledge Panel.
Second, your brand may show as an appropriate answer to some non-branded queries. In the grand scheme of things, schema markup is a critical component of structured data that enables the semantic web and search. In layman’s words, it enables URLs to communicate the true meaning of their content to machines such as the Googlebot.
Schema FAQ
Why use structured data for SEO?
Structured data is crucial for SEO because it helps Google understand what your pages and website are about. To show a page in the search results, Google must first determine what it is about. Using structured data is like communicating to Google and telling it what your site is about. This will boost your rankings.
Furthermore, structured data will alter the appearance of your snippet (search results). It will provide your consumer with extra information — more precise details. This increases the chance of a consumer clicking on your results. More clicks will lead to even higher ranks in the long run! We’re seeing more and more of it.
What is a schema tag in SEO?
Schema.org (also known as schema) is a semantic vocabulary of tags (or microdata) that you can add to your HTML to improve how search engines interpret and display your page in SERPs.
Schema.org is the product of a partnership by Google, Bing, Yandex, and Yahoo! to assist you in providing the information their search engines require to interpret your content and give the best search results available at the moment. By including schema markup into your HTML, you may improve the way your page appears in SERPs by increasing the rich snippets that show beneath the page title.
Why is schema important in SEO?
When you utilize schema markup, Google can quickly comprehend the content of your webpage. As a result, your website receives a rich snippet and has the potential to become an entity in Google’s Knowledge Graph.
Knowledge Graph
Schema markup is also one of the primary sources of data for Google’s Knowledge Graph, which is a knowledge base of things and their relationships. The Knowledge Graph assists Google in better understanding users’ search queries, allowing them to offer more relevant results.
One big advantage of being featured in Google’s Knowledge Graph is that you will receive a knowledge panel when people search about your brand. Google defines knowledge panels as “information boxes that show on Google when you search for entities (people, places, organizations, and objects) on the Knowledge Graph.”
They are intended to provide you with a brief overview of information on a topic based on Google’s knowledge of accessible web content. Knowledge panels are an excellent method to bring all essential information about your brand in front of people who are actively looking for it.
Rich snippets
A rich snippet is a Google search result that includes additional information in addition to the URL and meta description. Rich snippets are frequently found in recipes, reviews, and events.
For example, if you search for “taco recipe,” you may find the following two results on the SERP:
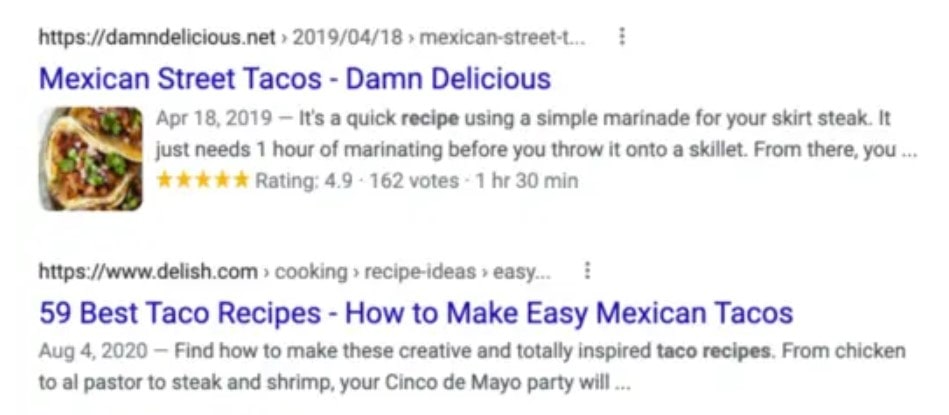
The first result in this case displays a rich excerpt. It contains details such as the recipe rating, cooking time, and a photo of the final dish. The information in rich snippets is frequently derived from structured data in the HTML of a page.
When you use schema markup to provide structured data to your webpage, Google is more likely to display rich snippets on the SERP when it appears in search results.
Rich snippets are more intriguing and attractive than standard search results, so providing Google with the information it need to generate a rich snippet may help boost exposure for your site and organic search hits.
While there is no clear proof that using schema markup automatically improves your results, structured data does assist gain more eyeballs on your content and business.
What is schema used for?
The most common application of schema markup is to add information about values in these categories:
- Medical entity
- Organization
- Creative work
- Event
- Person
- Place
The full hierarchy of values and things that may be marked up with schema tags can be found at Schema.org.
In layman’s terms, structured data from schema markup tells Google and other search engines about the content of a webpage. In turn, Google may use that information to offer searchers the most relevant results.
Product schema may be used by ecommerce websites to improve visibility by differentiating characteristics such as product name, brands, descriptions, reviews, product pictures, price, and availability. This increases exposure inside SERPs for a clear image of a certain product.
How many types of schema markups are there?
Search engines can only comprehend so much of your website when they crawl it. Some features, such as videos and reviews, are difficult to grasp. We can notify search engines what information a web page includes by using schema markup (structured data). The three most prevalent schema markup formats are supported by the most popular search engines:
1. JSON-LD
JSON-LD (JavaScript Objective Notation for Linked Data) is a structured data format for website tagging that is supported by the major search engines Google, Bing, and Yandex. It is Google’s preferred way of implementing structured data.
2. Microdata
Microdata is a collection of tags that allow you to mark up your website. These tags are immediately inserted to the HTML. Each tag set will have itemscope, itemtype, and itemprops.
The itemscope tag specifies which item is being referred. The itemscope tag is followed by the itemtype tag. Itemtype specifies the type of item that the microdata is referring to. It may be a local company or a recipe, for example.
3. RDFa
RDFa (Resource Description Framework in Attributes) is an HTML5 extension for marking up metadata in web pages. RDFa is similar to Microdata in that it uses tags inline with the current HTML.
Google announced JSON-LD as the recommended approach in 2015. This announcement was noteworthy since Google has not before shown a preference for one format over another. Until Google recommended that webmasters just annotate the visible text on the website. This is known as “inline” markup.
Here’s an example of Microdata markup inline.

On a web page, it might look like this: 687 Boise, Idaho 83702 River Run
This is a major change since if you are unfamiliar with in-line programming formats, such as Microdata, might be difficult to apply. It can sometimes limit the design of a web page. JSON-LD is hidden, thus it has no influence on how a web page is rendered, and it is considerably easier for webmasters to apply.
Summary
Hopefully, this article has given you a better understanding of schema.
Schema markup appears to be more frightening than it is. Most websites can quickly and simply mark up their material.
Adding markup to your sites not only makes your pages stand out in the SERPs with rich snippets, but it also helps to make the web genuinely connected. And a fortunate consequence is frequently the inclusion of your brand in the Knowledge Graph, which has several other advantages.
As more people click on your webpage — whether through a rich snippet or a knowledge panel — Google will discover that visitors who search for a related query or your brand name prefer your site over others. This informs Google that your page is an appropriate result for that particular search, which increases overall brand visibility.
Test out different schema markup tags on different pages to see how they influence your rankings and search traffic. Check out Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper tool to build your own code.
Hand off the toughest tasks in SEO, PPC, and content without compromising quality
Explore ServicesWritten by Adam Steele on December 19, 2021
COO and Product Director at Loganix. Recovering SEO, now focused on the understanding how Loganix can make the work-lives of SEO and agency folks more enjoyable, and profitable. Writing from beautiful Vancouver, British Columbia.





