12 On-Page Elements for SEO Success

Hand off the toughest tasks in SEO, PPC, and content without compromising quality
Explore ServicesGetting to the top of Google search has never been more competitive.
It’s also more involved and complex than it was a decade ago. That makes the job of SEO specialists and agencies much harder.
Nowadays you will see a lot of experts and agencies focusing on off-page and technical factors, such as link building and minifying code.
However, on-page factors are just as important, and we shouldn’t lose sight of that. To succeed in generating more organic traffic and improving search rankings, you need to manage all elements of SEO for your web pages.
That’s why we wrote this guide: to cover why on-page SEO is so important, and what elements you need to optimize to be successful.
What Is On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO refers to the elements on a page of your website that you can optimize to improve its search rankings. When you work on on-page optimization for each of these elements, you make it easier for search engines to crawl and understand your page.
In terms of basic optimization, it looks like this:
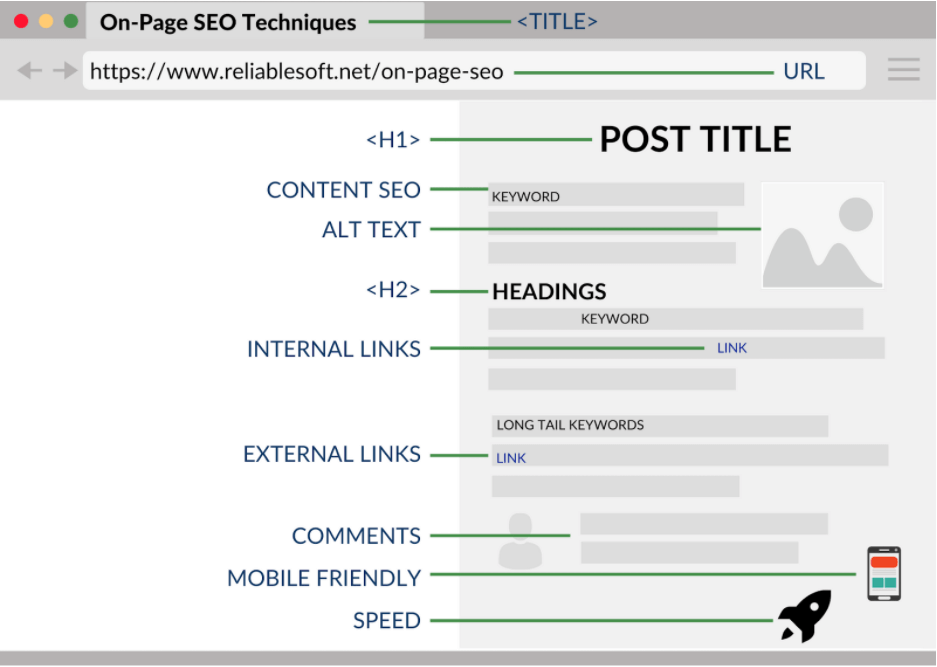
Source: https://www.reliablesoft.net/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/on-page-seo.png
When you combine all the on-page SEO factors together, they make up a crucial part of any SEO strategy. You can have tons of backlinks and a technically sound website, but without optimizing the on-page elements you still won’t be as successful.
What’s the difference between on-page and off-page SEO?
It’s pretty simple:
- On-page SEO describes specific elements of the pages on your website that you control.
- Off-page SEO, on the other hand, takes place beyond your website.
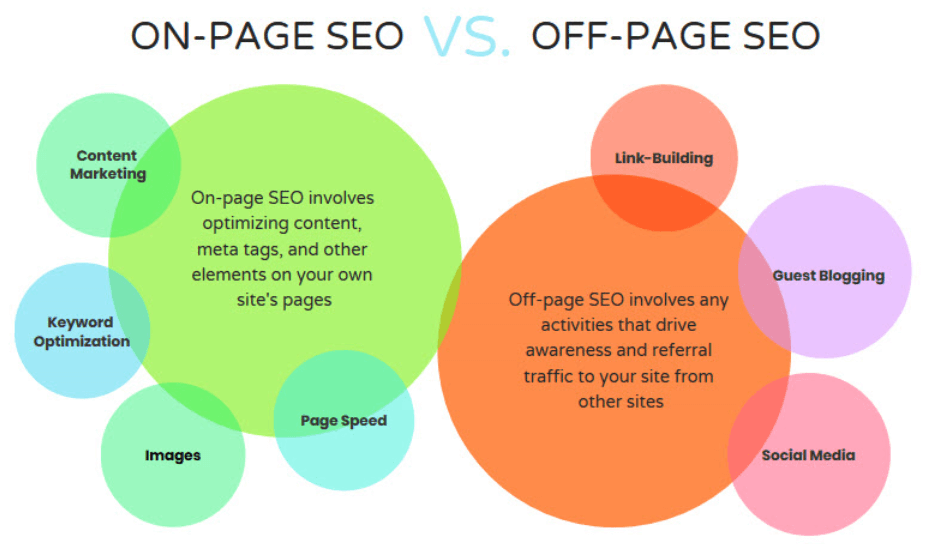
While there are some parts of off-page SEO that you can directly control, that isn’t the case a lot of the time.
For example, elements of off-page SEO include building links on other websites that point to your domain, social media, guest posts, and more.
For links and guest posts, and some social media signals, you will need other people to organically help you or agree to do so once you reach out to them.
When you follow a typical SEO roadmap you will wind up working on optimizing both on- and off-page elements. That is how you will have the most success with your SEO strategy.
Why On-Page SEO Is Important
When someone performs a search, Google will return results based on what it thinks is the most relevant and provides the best answer.
On-page SEO elements are what helps search engines understand what your website is about.
That way, they will know when your content is relevant and useful for a search and show your page in the results.
The biggest way to gain a competitive edge in the SEO world is knowing how to make search engines completely understand your content.
Search engines like Google are much better at understanding semantics and user intent, including:
- If the user is looking for information or shopping
- If the user is looking for local or organic content
- If the user is searching for something more relevant to a different term than they used
In the end, optimizing all of the on-page factors helps ensure your page is shown on more searches. That way you get more traffic, and better quality traffic that leads to more conversions.
12 On-Page Elements
Want to know what on-page SEO elements you need to optimize? We’ve put together this simple (but actionable) list of the 12 most important factors.
(Doing local marketing? You should check out this local SEO checklist)
You will need to work on optimizing all of these on every page on your website to have the greatest impact.
Let’s check them out below:
1. E-A-T
Expertise, Authority and Trustworthiness, or E-A-T for short, is a concept that Google uses to rank the quality of content on pages and websites.
For on-page SEO, this means that you need to convince Google that the information your website contains can be trusted as high-quality.
In general, Google wants to show users the highest quality and most trustworthy content at the top.
If you prove that you are an authority in your field and you are using your expertise to create high quality content, you will earn better rankings.
2. Title Tag
Every page on your website will have a bit of HTML code that is called the “title tag”. They act as the first signal to search engines and to users what the page is about. When someone performs a search, the clickable link in the search results is pulled from the title tag you set for the page.
Here’s what a page title tag looks like in the search engine results pages (SERPs):
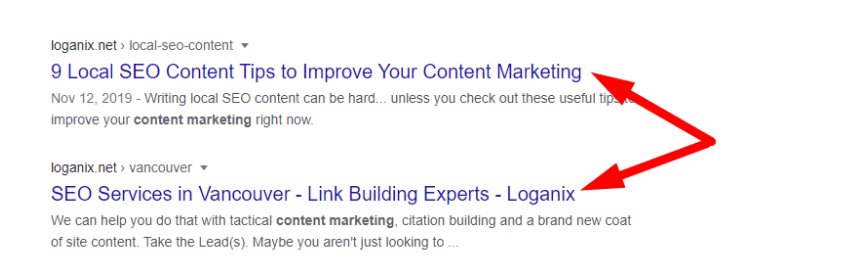
The title tag should introduce the topic of the page. By itself, title tags are not a significant on-page element.
However, it can become significant if you do not have any that are optimized. Here are some common mistakes or problems you should avoid when optimizing them on your site:
- They’re too long or too short
- They don’t include the main keyword or topic the page is meant to rank for
- You use the same title tag across multiple pages
For example, if you are optimizing a location page for your business it should absolutely include the city of that location. That way they will appear in local searches.
Or if you have a page selling a product, the product name should be in the title tag. These are quick and easy wins for on-page optimization.
3. Meta Description
The text that appears below the title tag in a search results page is called the meta description.
You have more characters to work with than a title tag, which you should use to elaborate on what the page is about.
Just like with title tags, they are not one of the most significant on page ranking factors by themselves. Not directly, anyways, according to Google themselves. However, a good meta description will help convince users to click on your page in the results (aka improve CTR).
That will help drive more traffic and conversions to your site.
A good local SEO strategy is to work in local signals into the description to help people and search engines
4. URL
The URL structure of a page is another small element that signals to search engines and users what it is about. It should be treated like the title tag: keep it short, and use the main keyword.
Here are two on page SEO examples of good and bad URL structure:
- Good = www.example.com/shoes/mens-hiking-boots/
- Bad = www.example.com/shop/products/23682sndy28.html
In the good example you can see that the page is about men’s hiking boots. In the second example, it could point to the exact same page but you would have no idea it’s for shoes. Search engines wouldn’t know that either, which will not help them trust in your content.
You should also pay attention to the hierarchy.
You can see that the category of the page is “shoes”, and that specific page is about hiking boots for men. This helps search engines understand that your page has a big focus on shoes, with multiple pages about specific types or brands.
5. Heading Tags (H1, H2, H3 etc)
Heading tags are a bit of HTML code that helps search engines and users understand what content is on a page at a quick glance.
Each page should have one H1 tag, and H2 tags to outline the main categories of information on the page.
You want your headings to introduce what the next section of content is about. The more specific you get, the more specific the heading tags should be.
Let’s take that example of the men’s hiking boots page. Here’s how you could structure the content using subheadings:
- H1 = Men’s hiking boots
- H2 = Brands
- H3 = Salomon
- H3 = Merrell
- H3 = Asolo
- H2 = Types
- H3 = Hiking shoes
- H3 = Day hiking boots
- H3 = Backpacking boots
- H2 = Brands
The structure of your headings should go from general to more specific. Setting them up this way helps search engines better understand the topical focus of the page: hiking boots.
It also helps them understand the specific information it contains (brands, types, etc). For users, headings also help make your content easier to read.
6. Alt tags (+ image optimization)
Alt tags are a bit of HTML code that helps search engines understand what pictures, videos and other media are on your page.
The issue is that while search engines can read and understand text, they are not yet able to read what is contained in an image or video.
So any time you include a piece of multimedia on your page, make sure you give it an alt tag. Treat it like a title tag for the specific piece of media.
For example, if your hiking boots page has an image of a pair of Salomon backpacking boots, you should set the alt tag to say alt=”Salomon backpacking boots”. That tag acts as text to tell Google what the image shows.
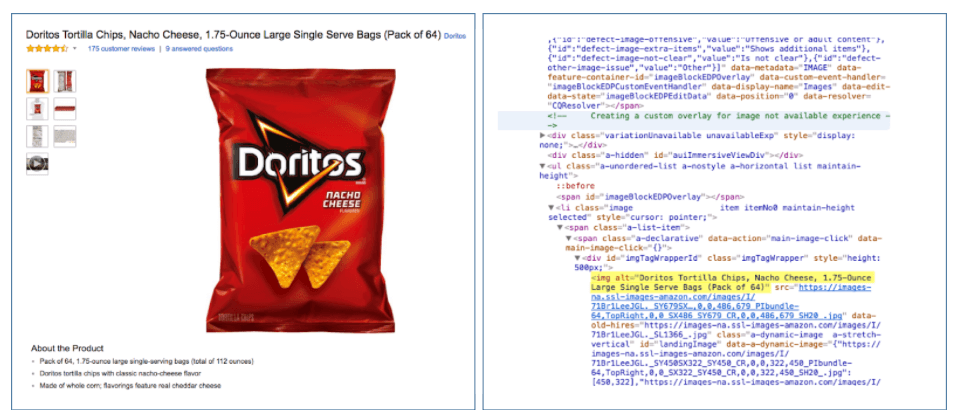
Source: https://moz-static.s3.amazonaws.com/learn/seo/Alt-Tag-page/alt-tag-image-8.png?mtime=20170315125711
It’s just another small way to help Google better understand what the topical focus of your page is. It’s also a way for people with vision issues to know what’s on the page if they use a screen reader, as they will read out the tag.
7. Keywords
Anyone who knows anything about SEO knows that keywords are important.
However, a common mistake is to try and create multiple pages to rank for one keyword. More is better, right?
Actually, the opposite is true.
When you have multiple pages trying to rank for one target keyword, search engines aren’t sure which page is the best one to show to a user.
They all wind up competing with each other, and in the end they will collectively rank lower than having one page focusing on it.
Forget about keyword density, LSI keywords and keyword stuff. Instead improve search engine rankings by using topic clusters. Group keywords/pages in terms of topics, using long-tail keywords to build topical relevance.
In plain English:
Create pages that are optimised for relevant keywords and then group them together so searchers (and Google) can find them.
8. SEO Content
All of the elements mentioned above are helpful, but in the end the most important on-page element that will affect your rankings is the content.
We touched on this earlier in regards to the E-A-T principle that Google follows, but there’s more to it than that.
Good content, whether it’s for organic traffic or local SEO content, shouldn’t just be authoritative and trustworthy. Content that is optimized for SEO should also:
- Be interesting and cover information that people actually want to read about
- Encourage engagement with readers so they interact with the page or click on other pages
- Be something that people want to link to and share on social media
- Be original – you should avoid duplicate content across your site
Even if you have content that is written by the foremost expert in the field, it won’t rank as the #1 result if it doesn’t achieve that.
If it’s a solid block of dry, boring text on a topic that only a small handful of people will understand or find interesting, it won’t get any traction.
9. Internal linking
Another important on-page ranking factor is having internal links to other pages on your website.
Having internal links helps search engine crawlers find more related content to a page. This relevancy (using descriptive anchor texts) helps them better understand the general focus of your website.
They also help the real people who browse your website. When you have links to related content to provide more context or information on a topic, people are likely to click on them to learn more.
That engagement keeps them on your site for longer, which is another positive signal to Google that they like and trust your content.
10. Page speed
Page speed has become a major ranking factor used by Google.
This is something they tie into the user experience. There are plenty of studies that show how page load and longer loading times leads to more people abandoning the page before it ever loads.
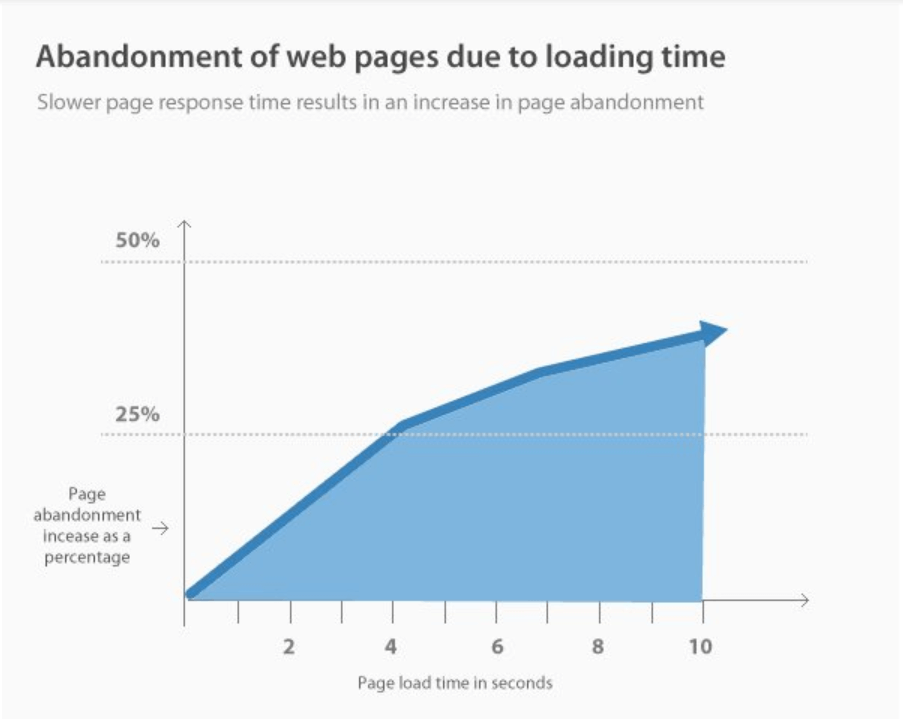
There are many tools, free and paid, that you can use to test the loading speed of a specific page on your site. Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool is a good one for quick tests.
There are a lot of elements that can affect site speed. But it is absolutely worth investing the time and effort into improving load time and making sure your pages load quickly.
11. Mobile-friendliness
Another major ranking factor for a page is how friendly it is for people viewing it on their mobile devices. This is called “mobile-friendliness”.
There’s not much point in having great content if users are struggling to view it on their phones.
More than 50% of all online traffic is now done on phones. As a result, Google now indexes websites based on their mobile pages — not their desktop pages anymore.
To have a “mobile-friendly” page, it needs to be easy to read and function properly. A common issue with a page developed for desktop first, is that when it gets adjusted for mobile that text or images become too small to see. Or buttons and other interactive elements don’t work, become hidden or broken, and so on.
There are tools that will show you how mobile friendly your page is. Once again, Google has a Mobile Friendly Test tool that you can use to check yours. If it rates poorly, you know you have some adjustments to make.
12. User Engagement
We’ve touched on the importance of having users engage with your content elsewhere. Google uses behavioural data to see how engaged readers are with your pages. If they’re engaged, it tells Google that your content is high quality, interesting, and trustworthy to real people.
On the other hand, if it does not engage with your audience then Google will assume it’s low quality or not what users for a given search want to see. They will reduce the ranking of that page over time if it is not fixed.
Examples of engagement includes the following:
- Users click on another page to read more
- Users interact with a tool you created
- Users click to play a video
- Users stay on a page for a long period of time
In general, you can tell how engaged people are with a page based on its bounce rate. If a high percentage of users leave the page without any of those engagements, that’s a bad sign that you need to figure out and fix.
Keep in mind that there are a lot of potential issues that can affect the bounce rate. Page speed, for example, can lead to people bouncing before the page ever loads. A poor mobile design that’s difficult or impossible to read or use will also increase the bounce rate.
Actionable SEO insights 🔍
Give us your site (or clients) and we’ll analyze the site’s SEO elements (on-page, URL equity, competitors etc), then organise this data into an actionable SEO audit.
Summary
These on-page SEO elements will collectively have a major impact on your website’s rankings.
While it is important to make sure the technical SEO and off-page elements are also optimized, you should not ignore the on-page factors.
Many of these elements will not significantly affect your search engine optimization on their own, they will when taken as a collective unit.
There is a high amount of synchronization between them all, such as how SEO content, page speed and mobile friendliness all affect each other.
When you have a website with pages that have great optimization, your pages will rank higher and earn more organic traffic, users will engage with them more, and lead to more conversions.
Hand off the toughest tasks in SEO, PPC, and content without compromising quality
Explore ServicesWritten by Jake Sheridan on October 13, 2020
Founder of Sheets for Marketers, I nerd out on automating parts of my work using Google Sheets. At Loganix I build products, and content marketing. There’s nothing like a well deserved drink after a busy day spreadsheeting.





