What Is 304 Not Modified? +Page Load Time & SEO Benefits
Hand off the toughest tasks in SEO, PPC, and content without compromising quality
Explore ServicesThere are quite a few different HTTP response codes, all representing something slightly different. Among them is the 304 not modified status. The topic we’re about to tackle together.
Here’s what you’ll learn by the end of this read:
- A straightforward explanation of the “What Is 304 Not Modified?” question.
- Insights into how the 304 status code is pivotal for optimizing web performance.
- Practical tips for effectively using and troubleshooting the 304 Not Modified response.
What Is the 304 Not Modified Status Code?
Think of a 304 Not Modified HTTP response code as a web server talking to your browser. The server might say, “Hey, the web page you’re requesting hasn’t been modified since the last time you visited. No updates, no tweaks, nothing new to see here, nada.” So, instead of the server sending the content again, chewing data, increasing server strain, and forcing the browser to load the page from scratch, the server simply lets your browser know that the version of the resource stored in its cache is still up to date and is fine to be reused.
Learn more: Interested in broadening your SEO knowledge even further? Check out our SEO glossary, where we’ve explained over 250+ terms.
How Does the 304 Not Modified Status Code Work?
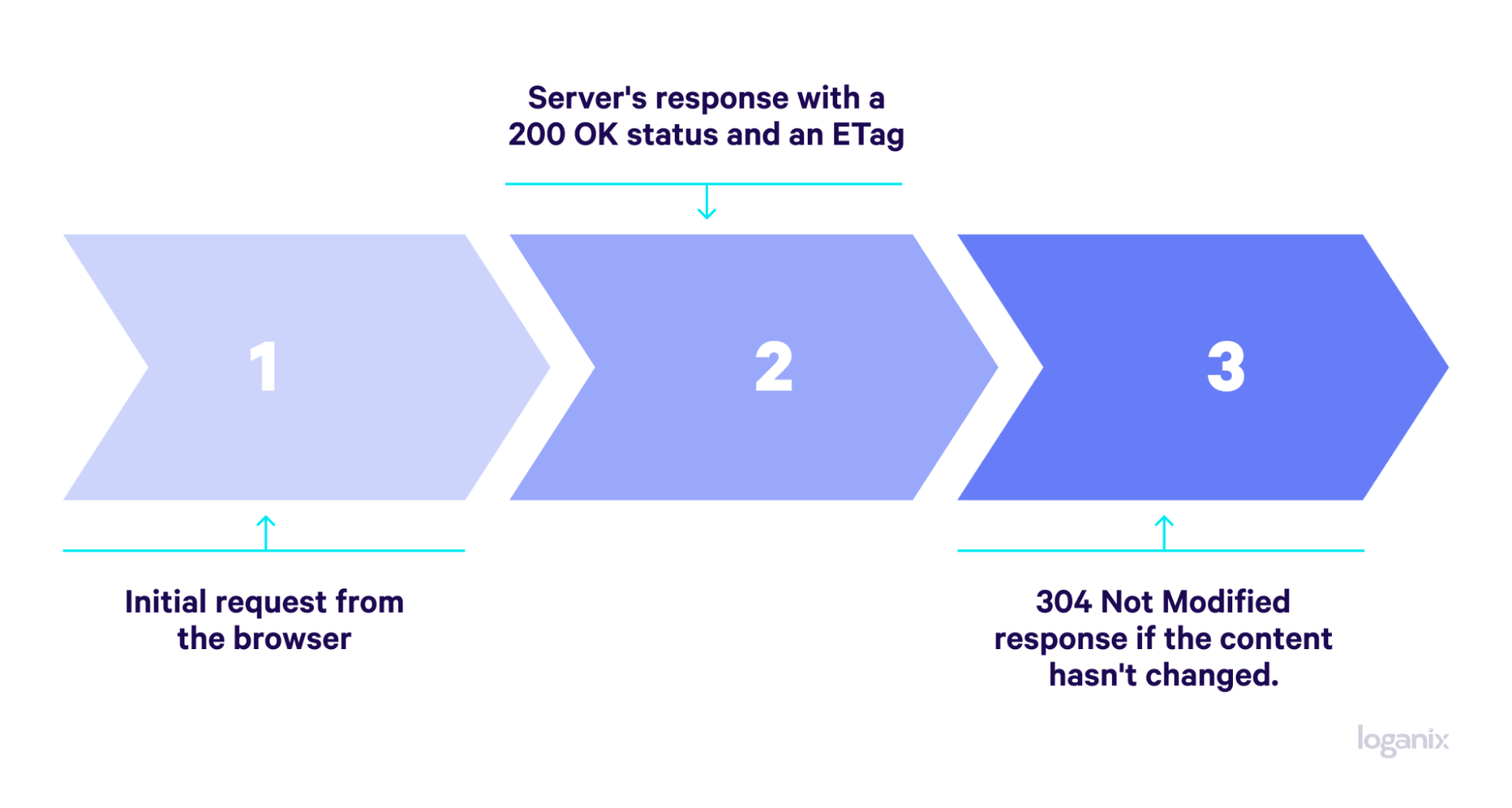
In layman’s terms, here’s the process:
Initial Request and Response
When a client (that’s your browser) requests a resource (like a web page or an image) for the first time, the server responds with a 200 OK status, indicating the successful retrieval of the information. Along with the resource, the server sends an ETag (Entity Tag), which is like, let’s say, a fingerprint of the content. The client also notes the time of the request.
The Role of Conditional Requests
Future requests for the same resource? The client aims to check if there have been any updates. It sends a conditional request, which includes special headers: “If-None-Match” and “If-Modified-Since.”
- If-None-Match checks against the resource’s ETag. A matching ETag means the resource hasn’t changed, signaling the server to respond with a 304 Not Modified status.
- If-Modified-Since looks at the date and time of the last request. If the server’s content hasn’t changed since then, it again responds with 304 Not Modified.
Determining Which Header to Use
When both headers are present, If-None-Match takes priority. Why? The ETag provides a more precise check than the date and time comparison, which ensures the client uses the most accurate version of the resource.
Client-Side Action on Receiving 304
Upon receiving a 304 Not Modified response, the client knows to use the version of the resource it has cached. Browsers cache resources to minimize the amount of data transferred over the network—a practice that conserves bandwidth and speeds up the web experience by avoiding unnecessary downloads.
Learn more: common website errors.
Why Is 304 Not Modified Important?
We’ve briefly touched on the benefits of a 304 status code, but let’s tease them apart further:
Bandwidth Conservation
Imagine every web page visit like having to redownload photos from your latest vacation every time you want to show a friend (Apple, I’m looking at you). Sounds very inefficient, right?
Not with 304s on the case. As I explained, if the content on a web page hasn’t changed, the server will simply remind your browser that it already has a copy. It eliminates the need for data retransmission and, in the process, saves bandwidth and reduces the load on web servers, allowing them to serve more users efficiently.
For websites with high traffic volumes, the bandwidth savings can be substantial, leading to cost reductions and keeping budgets happy.
Strapping Turbo Boosters to the World Wide Web
Time is money, and waiting for web pages to load is definitely not how you or, if you’re a website owner, your visitors want to spend it. 304 to the rescue once more. Reusing cached content, 304 status codes allow websites to load at a fraction of the time it would take to load resources—like images, CSS, and Javascript files—from the server, which, in some cases, could be located on the other side of the world.
Cached web pages translate to quicker information access, smoother navigation, and happier visitors.
Crawl Efficiency Benefits
Search engine web crawlers like Googlebot are constantly sniffing out new content to add to the company’s index. But, as you can imagine, with so much online content being published all of the time, search engines like Google have to conserve crawl resources. They achieve this by allocating each website a crawl budget which determines how many pages Googlebot will visit and index on a website within a given timeframe.
To conserve a website’s crawl budget and not waste it on recrawling web pages that haven’t moved or been changed in any way, website owners can use, you guessed it, a 304 not modified status code. With 304s in place, Googlebot will avoid unchanged web pages and save the crawl budget for new or updated pages.
Think of the practice like a limited grocery budget—by avoiding unnecessary purchases (redundant crawls), you have more resources to invest in the “good stuff” (fresh content) that attracts both search engines and users.
304 Not Modified FAQ
Q1: Should I Disable 304 Not Modified Responses on My Website?
Answer: I wouldn’t. Users and search engines both appreciate efficiency. 304s make browsing faster and save data, keeping everyone happy. Focus on creating fresh content instead of messing with a system that works.
Q2: Can I Customize the Behavior of 304 Not Modified Responses?
Answer: While you can’t rewrite the 304 code itself, you can give it some helpful guidelines using server-side tools called “caching control headers.” Think of them as sticky notes telling browsers and servers how long to hold onto cached content before checking for updates.
H3: Q3: Is 304 Not Modified Good or Bad for My Website?
Answer: A 304 is good news! It means your site loads faster and uses less bandwidth, improving user experience and potentially SEO. However, too many 304s could indicate static content, hindering search engine visibility. Aim for a balance and update content regularly.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Optimizing for website speed and search engine optimization goes beyond 304s alone. It takes a multifaceted approach. Something that’s centered around fine-tuning your site’s performance, broadening your content’s reach, and building a robust backlink profile to be proud of.
That’s where a team of SEO professionals like Loganix comes in. We use data-driven insights and tried and tested strategies to boost your website’s online presence and drive meaningful results.
So what do you think? Ready to take your SEO to the next level?
🚀 Visit our SEO services to learn about how Loganix will help you achieve your online goals. 🚀
Hand off the toughest tasks in SEO, PPC, and content without compromising quality
Explore ServicesWritten by Aaron Haynes on March 25, 2024
CEO and partner at Loganix, I believe in taking what you do best and sharing it with the world in the most transparent and powerful way possible. If I am not running the business, I am neck deep in client SEO.





