What is a Crawler? Exploring the Powerhouse of Web Indexing
Hand off the toughest tasks in SEO, PPC, and content without compromising quality
Explore ServicesNearly half of all web traffic is generated by the relentless efforts of web crawlers, with Google’s very own crawlers, known as Googlebots, accounting for an impressive 28.5 percent of all bot-driven traffic.
These numbers unveil a foundational principle of the online world: a website’s visibility and success hinge on its crawlability. If a site cannot be easily crawled, it remains hidden from search engines, unindexed, and, consequently, unranked in search results.
But what exactly does it mean for a website to be “crawlable”?
To get you up to speed with web crawlers, in this guide, we
- define “What is a crawler?”
- explore how they work and their importance,
- and break down the best tools and applications for web crawling.
What Is a Crawler?
While a web crawler goes by many names—spider, spider bot, web spider, web bot, or simply bot—what doesn’t change is its core purpose: to browse the contents of the World Wide Web with minimal human intervention. A king of set-and-forget kind of deal. You know, automated. And unlike human browsing, which is driven by individual curiosity or specific needs, web crawlers follow links, explore web content, and create a comprehensive index, all with precision and efficiency.
Learn more: Interested in broadening your SEO knowledge even further? Check out our SEO glossary, where we’ve explained over 250+ terms.
Different Types of Web Crawlers
While our primary focus in this guide will be on search engine crawlers and their impacts on search engine optimization (SEO), we’d be remiss if we didn’t mention that web crawlers come in various types, each serving specific functions:
- eCommerce crawlers are employed by online retailers to collect product information and compare prices.
- SEO crawlers like Screaming Frog are used by SEO professionals to analyze and optimize websites for search engines.
- Social media crawlers gather data from social media platforms for insights and analysis.
- News crawlers aggregate news from various sources for platforms like Google News.
How Does a Web Crawler Work?
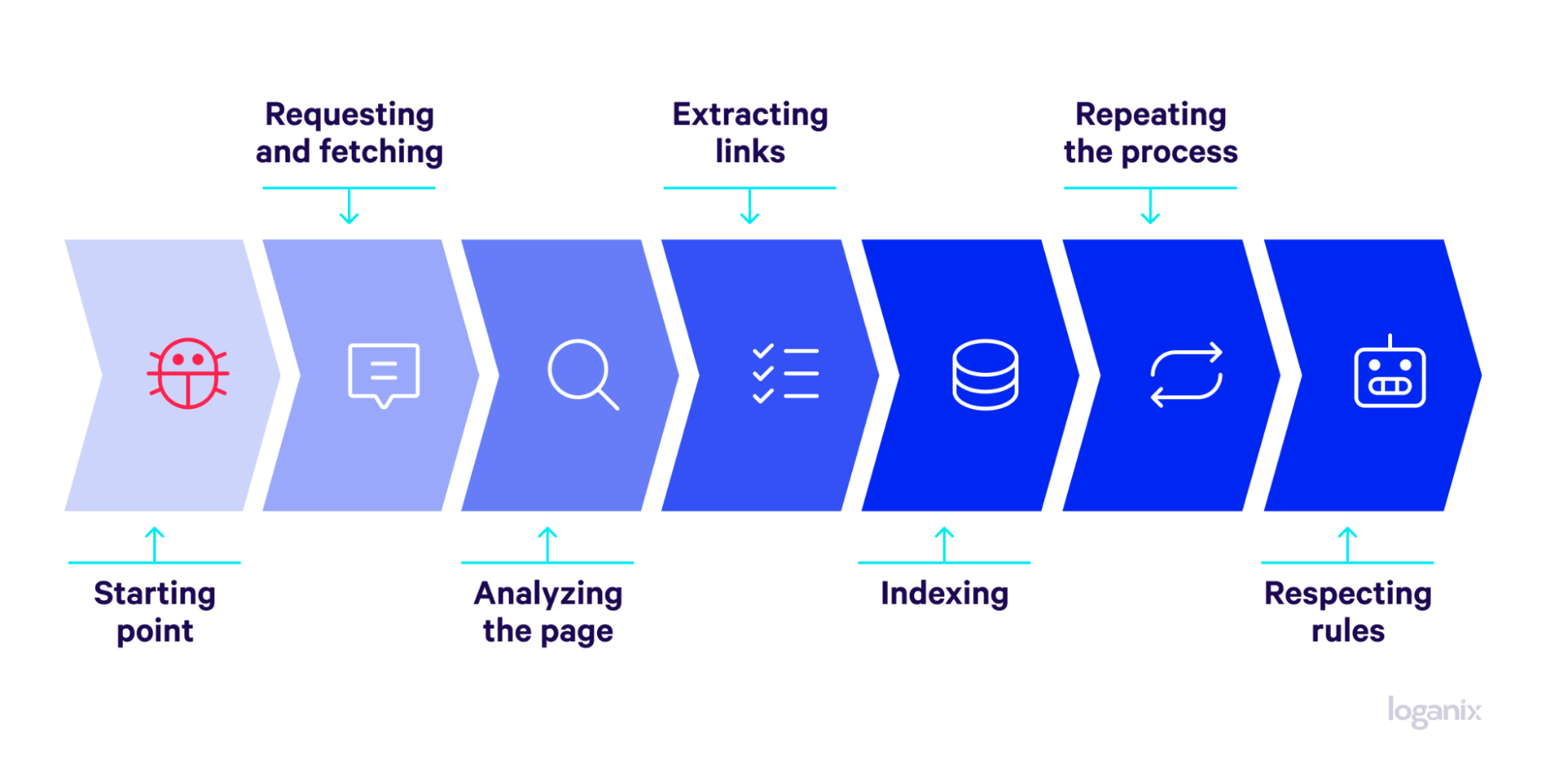
In the context of search engines, here’s a quick step-by-step breakdown of how web crawlers operate:
- Starting point: Crawlers begin with a list of URLs known as seeds or a seed URL. These seeds serve as the starting points for the crawl.
- Requesting and fetching: The crawler sends a request to the URL’s web server. Upon receiving permission, it fetches the page content.
- Analyzing the page: Web crawlers execute web scraping by meticulously scanning a web page’s content, meta tags, links, and other integral elements.
- Extracting links: The crawler extracts all the hyperlinks on the page and adds them to a queue of URLs to be crawled next.
- Indexing: The content is indexed and stored in a database, making it searchable by search engines.
- Repeating the process: The crawler moves on to the next URL in the queue and repeats the process.
- Respecting rules: Throughout this process, ethical crawlers adhere to rules set by website owners in the robots.txt file, which may include restrictions on what can be crawled.
Why Are Crawlers Important?
Having explored what web crawlers are and how they operate, why don’t we delve into why they are so crucial, particularly in the context of SEO, search indexing, and the user experience?
Importance of Web Crawlers for SEO
Web crawlers act as the gatekeepers of online visibility. Without their acts of service, the chance a website would secure the amount of visibility it can enjoy from search results would be very slim, limiting its reach and potential:
- Visibility: By crawling and indexing content, web crawlers ensure that websites appear in search results, connecting them with potential visitors.
- Competitive edge: SEO professionals leverage web crawlers to analyze competitors’ sites, gaining insights to optimize their own sites and stay competitive.
Role in Search Indexing
While we’ve touched on the process of indexing, it’s worth emphasizing the strategic importance of web crawlers in this area:
- Freshness: Web crawlers continually discover new or updated content, keeping search results current and relevant.
- Authority: By analyzing links between pages, crawlers help search engines understand the relationships and authority of different websites, influencing how they rank in search results.
Learn more: how to index your website on Google.
Impact on Website Performance and User Experience
Web crawlers don’t just affect how websites appear in search results; they also influence how websites perform:
- Performance: Poorly managed crawling strain server resources, slowing down the site. Proper crawling guidelines can prevent this issue.
- User experience: By ensuring that search engines have accurate information, web crawlers contribute to a positive user experience, guiding users to the content they seek.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What’s the Difference Between a Website Crawler and a Web Scraper?
A Website Crawler and a Web Scraper serve distinct purposes:
- Website Crawler: Also known as a web crawler or spider, it systematically browses the internet to discover and index web pages. It’s like mapping the digital landscape, identifying content and links across the World Wide Web.
- Web Scraper: A web scraper extracts specific data from web pages. It’s more focused on mining detailed information, such as product prices or reviews, from targeted web pages.
Q: What is Crawl Budget in SEO?
A: Crawl Budget refers to the number of pages a search engine’s crawler will visit and analyze on your website within a specific time frame. It’s determined by the crawl rate (how fast the crawler scans pages) and crawl demand (how often your site needs to be crawled). Managing your crawl budget ensures that search engines index your most important pages efficiently.
Q: How Do I Increase Google Crawl Rate?
A: Increasing Google’s crawl rate can be achieved by:
- Improving Site Speed: Faster-loading pages encourage more frequent crawling.
- Updating Content Regularly: Fresh content attracts more frequent visits from crawlers.
- Using a Sitemap: Submitting a sitemap through Google Search Console helps crawlers find your pages.
- Avoiding Crawl Errors: Fixing broken links and server errors ensures smooth crawling.
- Optimizing Robots.txt: Properly configuring “robots.txt” allows crawlers to access essential pages.
Q: What Is the Difference Between Crawling and Indexing in SEO?
A: In SEO, crawling and indexing are two distinct stages:
- Crawling: This is the process where search engine crawlers (or spiders) explore your website, following links and reading content to understand the structure and content of your site.
- Indexing: After crawling, the search engine stores the gathered information in an index, a massive database of all the content it has found. Indexing makes the content searchable and allows it to appear in search results.
Crawling identifies and reads the content, while indexing organizes and stores it for retrieval in search results.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Ensuring that your website is crawlable, indexable, and optimized requires a comprehensive approach. That’s where our SEO audit services come into play.
🚀 Don’t wait—discover how Loganix’s SEO audit services will provide the insights, guidance, and support you need to take your website’s visibility to the next level. 🚀
Hand off the toughest tasks in SEO, PPC, and content without compromising quality
Explore ServicesWritten by Aaron Haynes on December 28, 2023
CEO and partner at Loganix, I believe in taking what you do best and sharing it with the world in the most transparent and powerful way possible. If I am not running the business, I am neck deep in client SEO.





