What Is a Manual Action?

Hand off the toughest tasks in SEO, PPC, and content without compromising quality
Explore ServicesPeople who would try to exploit search algorithms and discover the easy road to the top of search results have been born since the first search engine was launched in the 1990s. This has created an issue for search engines that want to offer the best results to users, yet spam websites always come out on top.
As a consequence, Google improved its algorithm to better analyze websites for dubious methods and quickly spot spam. And, in order to keep these websites from hurting user experiences, Google began hitting spam websites with manual actions.
Assume you get to work one morning, open Google Analytics and your rank tracking tool, and everything is zero. You sipped your coffee and began your investigation. Is it possible that there is a problem with the tracking code? However, there is nothing wrong with it.
Then it hits you. You know you’ve been punished. Months or years of labor might be lost in the blink of an eye.
Manual actions can drive SEO professionals insane.
If you’re reading this, I hope it’s because you want to learn more about manual actions, not because you’ve been hit by one. Let’s get this party started!
What Is a Manual Action?
Google imposes a manual action or punishment on websites that engage in unethical tactics that violate its policies. These methods, known as Black Hat SEO, aim to influence search engine rankings.
Google uses hundreds of human reviewers to verify if websites conform with Google’s Webmaster Quality Guidelines in order to evaluate whether a website warrants a manual action. Google’s algorithm updates are effective at identifying spam and, for the most part, automatically doing a clean up.
Google also checks sites for situations when its standards and guidelines are not followed in order to improve the quality of search results. These instances are more difficult to identify algorithmically and necessitate a manual inquiry by a human, thus the name “manual action.”
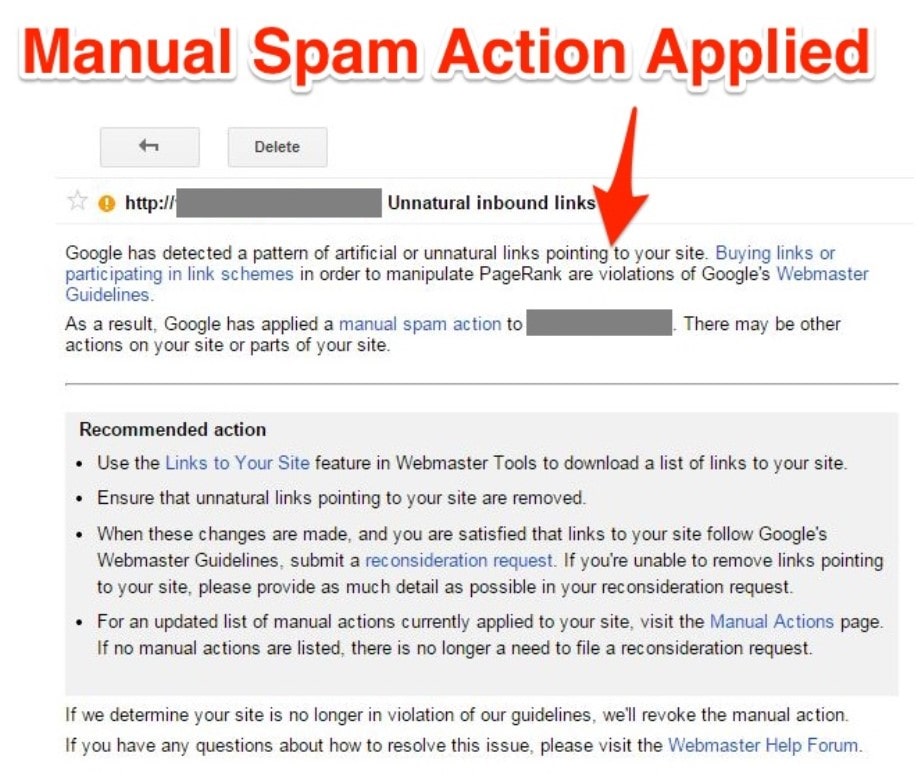
How can you spot Google manual actions? The Google Search Console tool has all of the essential information. Sign in to Google Search Console, navigate to your property, check the Security & Manual Actions area, and then view the Manual Actions report to identify Google manual actions.
There are 2 types of manual actions:
- Partial Matches (partial de-indexing)
If Google discovers pages that violate best standards, it may de-index those specific URLs. As a result, they will no longer appear in search results. This may be done to a page, sub-domain, forum, or any other domain area. A partial match action is usually the greatest option for webmasters who are dealing with spam assaults because the domain is still operational and visitors can still reach your site. It is still critical to try to resolve the situation and lift the action as soon as feasible.
- Whole Site Matches (total de-index)
If the issue is shown to be more widespread than a few important URLs, Google may de-index the entire site. This is a severe penalty, however it can be restored if the site follows webmaster rules. When a site flagrantly violates standards by concealing content, diverting visitors, or exposing users to harmful information, whole site matches are typically enforced.
If your site is facing a whole-site match, you should think about what got you there and whether you need to change direction.
The word actually refers to the punishment issued on a site for breaching Google’s rules, which might result in the removal of all or part of a site’s content from Google’s index.
Websites with thin or duplicate content, keyword-stuffed material, poor loading speeds, or a lack of backlinks or inbound links may be penalized by algorithmic penalties like as Panda, Penguin, and Hummingbird. With this type of punishment, you will still rank in search results, but significantly lower.
List of Manual Actions & How You Can Fix Them
There is a long list of offenses that might result in a manual action punishment. Here are a few examples of more frequent ones:
Spammy free hosting
Choosing free hosting services is a fantastic way to save money, but it may result in a manual action. If you choose a free hosting provider, your website will be housed on the same server as other websites. Even if your website is clean, spammers who share servers with you may have an impact on the entire server, and Google may take a manual action against all websites on that server.
Fix
Inform the technical support of the hosting business you are utilizing of the manual action. If nothing changes, we recommend that you switch to a secure hosting provider.
The structured data problem
Google can determine if structured data implementation violates the Structured Data Guidelines.
Fix
Comply with the standards by updating the current structured data markup on your website. To avoid mistakes, you might utilize the Structured Data Testing tool.
User-generated spam
This is a type of spam that is created by users. Websites that accept user-generated material, such as forums and blog comments, may be subject to this manual action if users flood the site with self-promotional language and links to irrelevant and spammy websites.
Fix
Use the “site:” search query to scan your website for harmful user content and delete it. [site:https://samplesite.com viagra] is an example. It is also preferable to avoid this by ensuring that every user-generated material is vetted before being accepted.
Unnatural links from your website
An artificial pattern of outbound links from your website may give Google the idea that you are selling links or engaging in link schemes.
Fix
Using the rel=”sponsored” element, you can identify paid or affiliate links.
Unnatural links to your site
Receiving this manual action indicates that Google discovered odd connection patterns to your page with the intent of manipulating PageRank. Excessive link exchanges and buying links from PBNs might result in a penalty.
Fix
Check the link report in Google Search Console for links that Google may consider suspicious. Create a text file and use the disavow tool to remove the disavow.
Cloaking and/or sneaky redirects
Cloaking is the process of altering a page’s code to display a different page than what was submitted to Google, whereas sneaky redirects trick people into being routed to a page they do not wish to visit.
Fix
Use webmaster tools like Google Search Console’s URL Inspection tool to examine how Google views the impacted pages. Fix the pages’ codes and content, and eliminate any dodgy redirection.
Thin content that adds no value
When it comes to content quality, Google has rigorous requirements. Google provides the following examples of pages with little or no added value:
- Content that has been scraped
- Low quality guest posts
- Content that is created automatically
- Affiliate pages that are too thin
- Pages that lead to other pages
Fix
Examine whether these pages can be enhanced and whether they can give value to users. Alternatively, you may use a robots.txt file to prevent Google from indexing certain pages, or you can use a noindex tag to remove them from SERPs.
Pure spam
Google discovered pages on your website that openly use webspam methods.
Fix
Check that all pages on your website follow Google’s Webmaster Guidelines.
Cloaked Images
Similarly to cloaking, Google offers manual action for cloaked images when it crawls an image on a website but it is shown differently to users.
Fix
Make certain that your website displays the exact same pictures to consumers as those seen in Google search results.
Keyword stuffing and/or hidden text
Excessively repeating a targeted term on a single page and/or concealing it by covering it with an image or making the text color white so it merges with the backdrop is a black hat SEO tactic.
Fix
Examine the HTML codes of the impacted sites, as well as the CSS style, for buried text and excessive keyword repetition in the meta tags.
Mobile redirects that are deceptive
If a feature is designed particularly for mobile users, mobile users may view a distinct version of a webpage. However, there are times when mobile visitors are routed to a different URL using code or a script that pushes mobile users to click an ad.
Fix
If you were given this manual action and did not put it there on purpose, check to see if your website has been hacked or scan for malware.
Mismatch in AMP content
AMP, or accelerated mobile pages, is a mobile-friendly version of a website. The content of an AMP version of a webpage should be the same as the content of the original webpage.
Fix
Ensure that the AMP page is canonicalized to the appropriate web page. The manual action for AMP content mismatch will not have a significant impact on your rankings, but Google will remove the AMP version from mobile search results and display the original webpage instead.
Manual Action FAQ
What is the Google manual penalty?
A Google penalty indicates that your site is no longer featured in search results or that your ranking for your chosen keywords has decreased significantly. When your website receives a Google penalty, your target audience will be unable to discover you. When you become invisible to your target audience, your traffic and, eventually, your income suffer.
Some of the primary things Google searches for include link building schemes, black hat methods, and harmful malware.
Any website is vulnerable to this type of attack. A Google penalty might arise from well-intentioned and sincere efforts to enhance your site’s rating. However, once you’ve received a Google penalty, it’s not easy to regain your excellent rating and return to Google’s good graces.
Loganix may assist you in recovering from a Google penalty. We have a specialized staff that will examine your site and make the required modifications to get you back to the top of search engine rankings.
Want to stay secure even if you haven’t gotten a Google penalty?
Our professional internet marketers remain up to date on Google’s continuously changing algorithms, ensuring that your site is always in good standing and does not fall out of the search results.
We know what search engines prefer to see as a top Google penalty repair provider.
How do I remove manual action?
- Read the Google notice message carefully, looking for highlighted penalization causes and possible solutions to the problem.
- Examine the issue. This procedure necessitates data collection and might take many weeks.
- Repair the problem, guarantee future Google Webmaster Guidelines compliance, and document all measures made.
- Along with the reconsideration request, include a brief and to-the-point justification that demonstrates your attempts to remedy the manual action penalty. Make certain that all assertions can be replicated.
- Do not negotiate or explain; instead, concentrate on what has been done to resolve the issue.
- Major modifications to the site should be avoided while the request is being handled. A site’s ranking in Google will not increase if it receives too many fluctuating search signals at the same time.
How do you recover from a manual link penalty?
Recovering from a penalty may be a time-consuming, complex, and unpleasant process. As a result, it is preferable to approach the procedure one day at a time.
Here are 4 simple steps you may take to get started without overburdening yourself or your team:
- Thoroughly research your penalty. Set aside an hour or two to research the penalty you received. If you’re still thinking, “but we didn’t do anything wrong!”… well, that needs to alter before you begin. If you aren’t sincere about getting better, your efforts will most likely be futile. Do some research on the penalty until you understand why you got it, what it implies for your future SEO strategy, and how others have recovered from it. If you can discover case studies, they can help you create your own recovery strategy. Moz, Search Engine Watch, and Search Engine Journal are excellent places to start.
- Coordinate your efforts. Set up a face-to-face meeting with an agency or SEO business that just handles a portion of your web marketing or development to unify your recovery efforts. After you’ve gone through the procedures in the next section, you’ll most likely want to allocate tasks to specific members of your team. If your recovery appears to be time-consuming and labor-intensive—for example, if you have hundreds of links to remove—consider developing a shared document where you can all “check in” and assess progress.
- Continue to work. We advise you to cease doing anything that may have led to the punishment. This does not, however, imply that you should quit working altogether. You most likely still have visitors and clients arriving to your site via other channels, and they may be unaware that anything is wrong. So keep filling orders, writing blog articles, and answering phone calls. Keeping up with your normal routine as much as possible may help take the “sting” out of the stress of recovering from a punishment.
- Take breaks whenever possible. Again, the rehabilitation process may be lengthy and difficult for you and your team. If you spend a week removing spammy links or rewriting thousands of words for your website, take some time to unwind or congratulate your team for their efforts. Purchase coffee for them, take them to the movies, or give them a few hours off on Friday afternoon. After you’ve completed these first stages, it’s time to get serious about your rehabilitation efforts.
Summary
Hopefully, this article has given you a better understanding of a manual action.
It’s not the end of the world if you’ve received a manual action from Google. You may have a lengthy road ahead of you in order to restore your website and regain your rankings. It is possible if you are honest about what went wrong and are willing to devote the time and money necessary to make things right again.
Simply because your site’s rating in search engine results has dropped does not imply that you’ve been penalized by Google. Your competition is rising by the day, and Google algorithms for ranking websites is continuously changing. When you suspect you have a Google penalty, you may really require enhanced search engine optimization tactics.
If you think that your site has been hit by a penalty, Loganix will conduct an audit to see if this is the case. If you do, we’ll take quick action to bring your site back into Google’s good graces. If you do not have a manual or algorithmic penalty, we may examine your site and advise you on all the measures you can take to enhance your rating.
Hand off the toughest tasks in SEO, PPC, and content without compromising quality
Explore ServicesWritten by Jake Sheridan on December 15, 2021
Founder of Sheets for Marketers, I nerd out on automating parts of my work using Google Sheets. At Loganix I build products, and content marketing. There’s nothing like a well deserved drink after a busy day spreadsheeting.





